Straight seam steel pipe requirements
Release Time:
2023-03-10
Welded steel pipes should be subjected to mechanical performance test, flattening test and flaring test, and must meet the requirements of the standard. The steel pipe should be able to withstand a certain internal pressure. If necessary, carry out a 2.5Mpa pressure test and keep it for one minute without leakage.
Welded steel pipes should be subjected to mechanical performance test, flattening test and flaring test, and must meet the requirements of the standard. The steel pipe should be able to withstand a certain internal pressure. If necessary, carry out a 2.5Mpa pressure test and keep it for one minute without leakage. The method of eddy current flaw detection is allowed to replace the hydrostatic test. The eddy current flaw detection is carried out according to the standard of GB7735 "Steel tube eddy current flaw detection inspection method". The eddy current flaw detection method is to fix the probe on the frame, keep a distance of 3~5mm between the flaw detection and the weld seam, and conduct a comprehensive scan of the weld seam by the rapid movement of the steel pipe. The flaw detection signal is automatically processed and sorted by the eddy current flaw detector. To achieve the purpose of flaw detection.
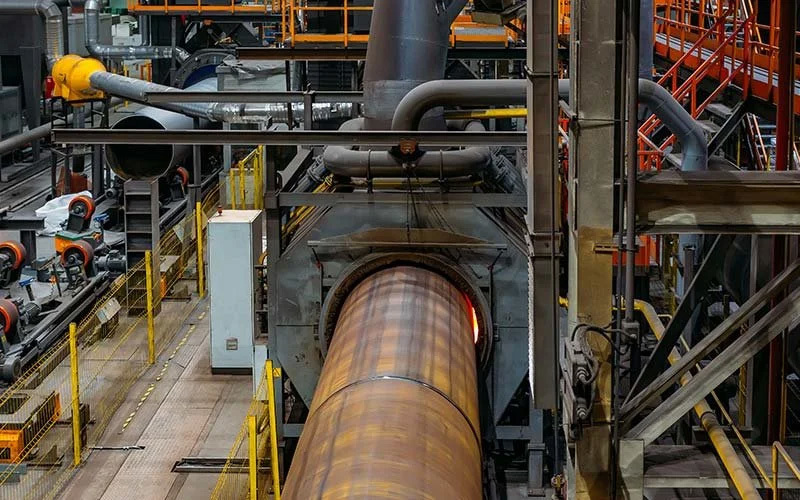
After flaw detection, the welded pipe is cut off according to the specified length with a flying saw, and is rolled off the production line through the turning frame. Both ends of the steel pipe should be chamfered with flat ends, printed with marks, and the finished pipes are packed in hexagonal bundles before leaving the factory.
The main processing methods of straight seam steel pipes are:
Forging steel: A pressure processing method that uses the reciprocating impact force of a forging hammer or the pressure of a press to change the blank into the shape and size we need.
Extrusion: It is a processing method for steel to place metal in a closed extrusion box and apply pressure at one end to make the metal extrude from the specified die hole to obtain a finished product with the same shape and size. It is mostly used for the production of non-ferrous metal steel .
Rolling: A pressure processing method in which the steel metal billet passes through the gap between a pair of rotating rolls (various shapes), and the cross-section of the material is reduced and the length is increased due to the compression of the rolls.
Pulling steel: It is a processing method in which the rolled metal blank (type, pipe, product, etc.) is pulled through the die hole to reduce the cross section and increase the length. Most of them are used for cold working.
Label:
Relevant Information